Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, is a condition where the glucose level in your blood drops below the standard range. While hypoglycemia is commonly associated with diabetes treatment, there are various other factors that can lead to low blood sugar in individuals who do not have diabetes. It is crucial to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia and seek immediate treatment to prevent any complications.
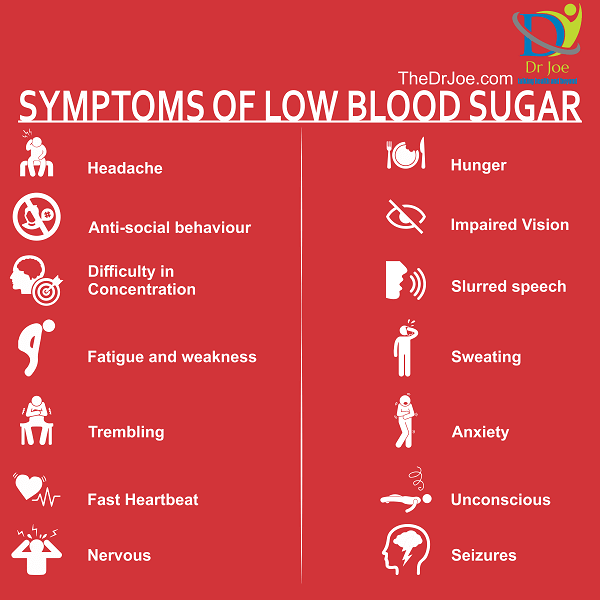
When blood sugar levels plummet, individuals may experience a range of symptoms indicating hypoglycemia. These symptoms can include shakiness, sweating, headache, hunger, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. As hypoglycemia worsens, more severe signs such as confusion, loss of coordination, and even seizures may occur. It is essential to be aware of these symptoms and seek medical attention promptly.
While hypoglycemia is more commonly seen in individuals with diabetes, it can also affect those without the condition. Some potential causes of low blood sugar in non-diabetic individuals include:
While hypoglycemia typically occurs when an individual has not eaten for a while, it can also manifest after certain meals. This type of low blood sugar, known as reactive hypoglycemia, may be observed in individuals who have undergone surgeries that affect stomach function, such as gastric bypass surgery.
Failure to address hypoglycemia promptly can lead to severe complications, including seizures, coma, and even death. Additionally, untreated low blood sugar can result in dizziness, falls, injuries, and an increased risk of dementia in older adults. It is crucial to manage hypoglycemia effectively to prevent these adverse outcomes.
For individuals with diabetes, following a comprehensive diabetes management plan is essential in preventing episodes of low blood sugar. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, carrying fast-acting carbohydrates, and considering continuous glucose monitoring can help reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. It is also vital to educate family and friends on how to respond to severe low blood sugar episodes.
For those without diabetes experiencing recurring hypoglycemia, working closely with a healthcare provider to identify and address the underlying causes is crucial. While consuming frequent small meals may provide temporary relief, a long-term strategy should focus on treating the root of the issue.
Low blood sugar can occur in individuals both with and without diabetes, necessitating prompt recognition and appropriate management. By understanding the potential causes of hypoglycemia and adopting preventive measures, individuals can effectively mitigate the risks associated with low blood sugar episodes. Seeking medical advice and adhering to personalized treatment plans are key in ensuring optimal blood sugar control and overall well-being.