Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
Iron is a crucial mineral that plays a vital role in the human body. Approximately 70% of the iron in our bodies is found in hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Iron is also essential for the production of myoglobin, a protein that supplies oxygen to muscles, as well as for the synthesis of certain hormones.
The daily recommended intake of iron varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and dietary preferences. For instance, vegetarians may need higher amounts of iron compared to individuals who consume meat. It is important to ensure that you are meeting the recommended daily intake of iron to support overall health and well-being.
Iron can be obtained from a variety of food sources, including lean meats, seafood, poultry, iron-fortified cereals, beans, lentils, spinach, and nuts. It is worth noting that there are two forms of dietary iron: heme iron, found in animal products, and non-heme iron, found in plant-based foods. Consuming vitamin C-rich foods alongside iron-rich foods can enhance the absorption of non-heme iron.
Iron supplements are available in various forms, such as ferrous sulfate, ferrous gluconate, ferric citrate, or ferric sulfate. These supplements can be beneficial for individuals who may have difficulty meeting their iron requirements through diet alone. However, it is essential to follow dosage recommendations and keep iron supplements out of reach of children to prevent accidental overdose.
Iron deficiency can lead to a condition known as iron deficiency anemia, characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin levels. Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia may include weakness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and a weakened immune system. It is crucial to address iron deficiency promptly to prevent further health complications.
Iron plays a critical role in various physiological processes, including supporting immune function, hormone synthesis, and oxygen transport. Adequate iron levels are particularly important during pregnancy to support maternal and fetal health. Infants and toddlers also require sufficient iron for proper growth and development.
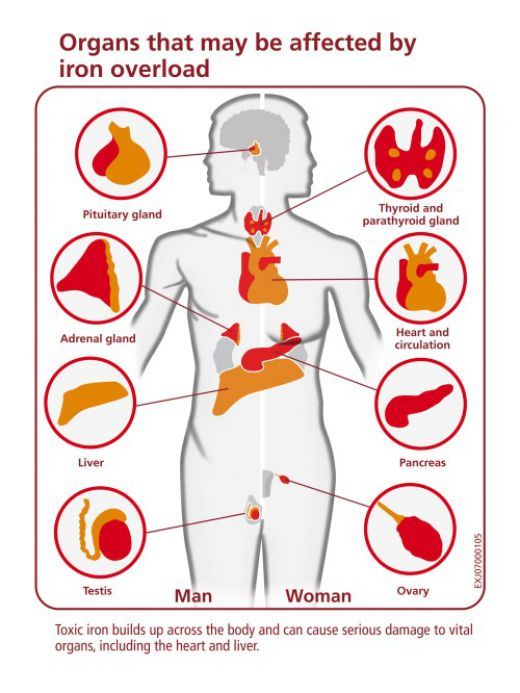
While iron is essential for health, excessive intake can have adverse effects. High doses of iron supplements can lead to gastrointestinal issues, organ damage, and even toxicity. Individuals with conditions such as hemochromatosis, characterized by excess iron absorption, should exercise caution when consuming iron supplements.
Iron supplements can interact with certain medications, affecting their absorption and efficacy. It is important to inform healthcare providers about any supplements or medications you are taking to prevent potential interactions. Additionally, timing the intake of iron supplements with other supplements, such as calcium, can help optimize absorption.
Consuming a balanced diet that includes iron-rich foods is key to meeting your body’s iron requirements. Pairing iron sources with vitamin C-rich foods can enhance iron absorption. However, if dietary intake alone is insufficient, iron supplements may be recommended under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
For personalized recommendations regarding iron intake and supplementation, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider, such as a doctor or registered dietitian. They can assess your individual needs and provide tailored advice to support your overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, iron plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including oxygen transport, immune function, and hormone synthesis. Maintaining adequate iron levels through a balanced diet and, if necessary, supplementation, is essential for overall health. By understanding the importance of iron and its impact on the body, individuals can take proactive steps to support their well-being.