Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents [hide]
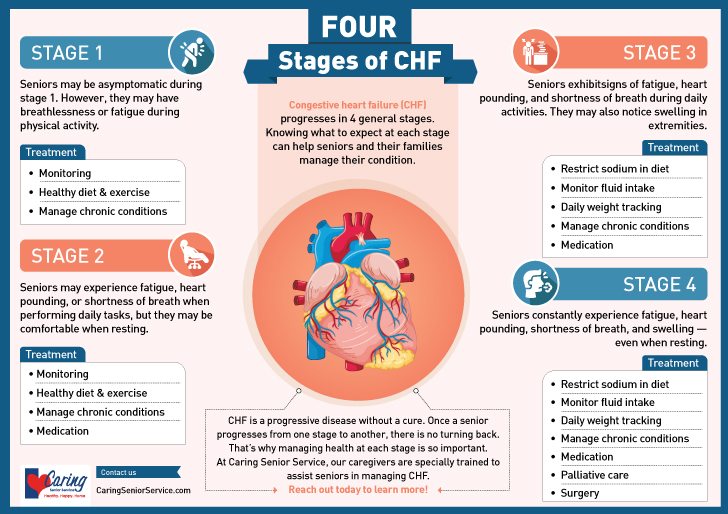
Congestive heart failure is a chronic condition that affects the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. It can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, making it crucial to understand the different stages of this condition. By recognizing the stages of congestive heart failure, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and well-being. Let’s delve into the four stages of congestive heart failure and what each stage entails.
In stage A of congestive heart failure, individuals do not exhibit any symptoms of heart failure. However, they are at a high risk of developing the condition due to underlying health issues such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or coronary artery disease. At this stage, the focus is on managing risk factors and preventing the progression of heart failure.
Individuals in stage A should work closely with their healthcare provider to address any potential concerns and adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle. This may include following a low-sodium diet, staying active, and taking prescribed medications to control underlying conditions.
Stage B marks the development of structural heart disease, such as reduced pumping function of the heart or an enlarged left ventricle. While individuals in this stage may not experience heart failure symptoms, they are at a higher risk of progression. Treatment at this stage typically involves medication to manage and prevent future complications.
Healthcare providers may prescribe medications like ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or beta blockers to help maintain heart function and prevent further deterioration. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to track any changes in heart health.
Stage C signifies the onset of heart failure symptoms, such as fatigue, breathlessness, or swelling in the extremities. Individuals in this stage may require more intensive treatment to manage their symptoms and improve heart function. Medications like diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and mineralocorticoid receptor blockers are commonly prescribed at this stage.
Aside from medication, healthcare providers may recommend additional interventions, such as implantable devices or cardiac resynchronization therapy, to support heart function. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and regular exercise, play a crucial role in managing heart failure symptoms in stage C.
Stage D represents advanced heart failure with significant symptoms that may persist even at rest. Individuals in this stage require specialized treatment options, including mechanical circulatory support, continuous inotropic infusion, cardiac transplant, or hospice care. The focus shifts to improving quality of life and managing symptoms effectively.
Healthcare providers will work closely with individuals in stage D to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on their unique needs and medical history. Advanced interventions may be necessary to support heart function and alleviate symptoms associated with severe heart failure.
Understanding the four stages of congestive heart failure is essential for individuals living with this condition. By recognizing the progression of heart failure and the associated symptoms, individuals can work proactively with their healthcare providers to manage their health effectively. From early intervention in stage A to specialized treatment in stage D, each stage of congestive heart failure requires a tailored approach to optimize heart function and quality of life.