Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
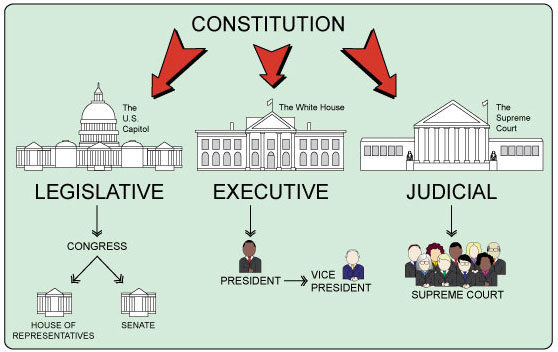
As of 2024, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the three branches of government in the United States. The Constitution of the United States divides the federal government into three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. This division is essential to prevent any single individual or group from having excessive power.
The system of checks and balances ensures that each branch of government can respond to the actions of the other branches. This mechanism is vital for maintaining a balance of power within the government. Here is how each branch provides checks and balances:
The legislative branch, which consists of the U.S. Congress, is responsible for creating laws. It is divided into two parts: the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress has the authority to determine the state’s operating budget, consider proposed amendments to the Constitution, and establish legislative districts based on population data.
The executive branch is headed by the President of the United States, who enforces the laws created by Congress. The President is elected by U.S. citizens and oversees the executive branch, which includes about 5,000,000 workers. The President has the power to veto legislation, nominate officials to positions in the government, and lead the country’s National Guard and police forces.
The judicial branch, led by the U.S. Supreme Court, interprets laws and administers justice. The Supreme Court consists of nine justices who hear cases related to constitutional issues. In addition to the Supreme Court, there are lower federal courts in each state that handle cases involving federal matters.
It is important to note that the three-branch structure of government is not exclusive to the federal level. State and local governments also operate with a similar framework. Under the Tenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, states have the authority to govern powers not granted to the federal government. State governments are modeled after the federal government and consist of executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
For instance, in Georgia, the state government mirrors the federal structure with its own legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The Georgia General Assembly, comprising the Senate and the House of Representatives, is responsible for creating and debating laws, determining the state’s budget, and considering proposed constitutional amendments. The executive branch in Georgia is led by the governor, who enforces laws, oversees the state budget, and fills vacancies in public offices.
Georgia’s judicial branch interprets state laws and administers justice through various courts, including the Supreme Court of Georgia and the Court of Appeals of Georgia. The Judicial Council, overseen by the chief justice of the Supreme Court, develops policies for the state courts. The judicial system in Georgia plays a crucial role in upholding the rule of law and ensuring justice for all.
Understanding the three branches of government at the federal, state, and local levels is essential for maintaining a system of checks and balances. By delineating the powers and responsibilities of each branch, the U.S. government ensures that no single entity can wield unchecked authority. As of 2024, this system continues to be a cornerstone of democracy in the United States.