Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
A sore throat, also known as pharyngitis, is a common condition characterized by redness, swelling, and pain in the throat, particularly when swallowing. It is prevalent in both adults and children, with various causes ranging from viral infections like the common cold to bacterial infections such as streptococcus pyogenes (strep A). Understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of a sore throat is essential for managing this discomforting condition.
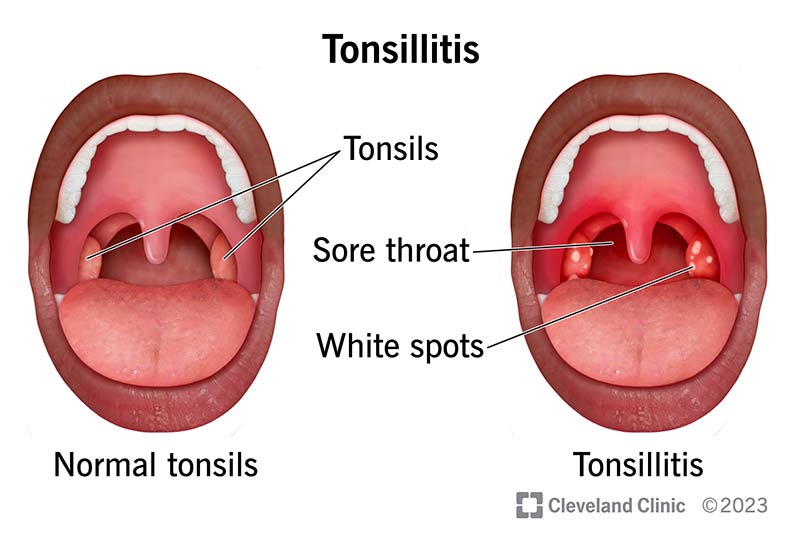
A sore throat typically presents as a scratchy or painful sensation in the throat, which can worsen with swallowing or speaking. Other symptoms may include difficulty swallowing, redness in the throat, white patches or pus streaks, runny nose, cough, fever, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, swollen tonsils, rash, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Children with a sore throat may also exhibit reduced appetite.
The primary cause of a sore throat is viral infections like colds, flu, COVID-19, or glandular fever. Bacterial infections, particularly streptococcus pyogenes (strep A), account for less than one-third of sore throats. Tonsillitis, mouth ulcers, and allergies can also lead to a sore throat.
If experiencing persistent or severe symptoms, it is advisable to consult a doctor for evaluation. A healthcare provider may conduct a physical examination, throat swab, and assess swollen glands to determine the underlying cause of the infection. Throat swabs can help identify specific viruses or bacteria responsible for the sore throat.
While most sore throats resolve within a week without treatment, it is crucial to see a doctor if symptoms persist for more than two days, accompanied by drinking difficulties, snoring, ear pain, or other concerning signs. Urgent medical care is necessary in cases of breathing difficulties, swollen neck, persistent rash, drowsiness, or unusual skin discoloration.
Self-care measures such as rest, hydration, warm saltwater gargles, and consuming soft foods can alleviate sore throat symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relief medications like paracetamol and ibuprofen can help manage discomfort. Antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial infections, while avoiding smoking and maintaining good hand hygiene can aid in prevention.
Most sore throats do not lead to complications; however, strep A infections can result in abscesses, rheumatic fever, or kidney issues. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent complications. Resources and support services are available to provide information and guidance on managing sore throat conditions.
Strep throat, caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria, is a contagious infection that primarily affects the throat and tonsils. Common symptoms include fever, pain on swallowing, redness, swollen tonsils, pus patches, and swollen lymph nodes. While strep throat is more prevalent in children, it can also affect adults, especially those in close contact with infected individuals.
Healthcare providers can conduct rapid strep tests or throat cultures to diagnose strep throat accurately. Antibiotics are the primary treatment for strep throat to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the spread of bacteria to others. It is essential to complete the full antibiotic course as prescribed and follow medical advice for recovery.
Preventive measures such as hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and staying home when ill can help reduce the risk of strep throat transmission. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and when to seek medical attention is crucial for managing strep throat effectively and protecting oneself and others from potential complications.