Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
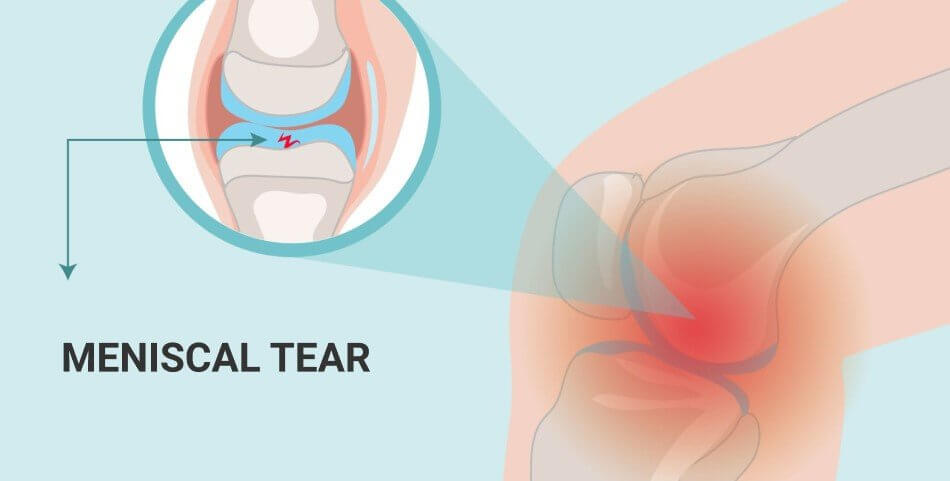
A torn meniscus is a common knee injury that can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness. The meniscus is a cartilage disc that acts as a cushion between the shin and thigh bones, providing stability to the knee joint. When the meniscus is torn, it can lead to a range of symptoms and may require medical intervention for proper healing.
Identifying a torn meniscus based on external appearance alone can be challenging. While severe cases may exhibit swelling and deformity in the knee, milder tears may not be visibly apparent. Swelling is a common sign of a meniscal tear, indicating fluid accumulation in the knee joint as a response to the injury. In some cases, the knee may look normal despite significant pain experienced by the individual.
Torn meniscus symptoms are crucial for early detection. Patients may experience a popping sensation at the time of injury, followed by knee pain, stiffness, and swelling. Twisting or rotating the knee can worsen the pain, especially during physical activities. From mild discomfort to the inability to bear weight on the leg, the range of symptoms can vary.
Diagnosing a torn meniscus typically involves a physical examination, where a healthcare provider will inquire about symptoms and conduct tests to assess the knee’s mobility. Radiological imaging studies, such as X-rays and MRI scans, are often ordered to confirm the diagnosis. X-rays help rule out bone injuries, while MRI scans provide detailed information about the type and location of the tear.
The treatment approach for a torn meniscus depends on various factors, including the tear’s size, location, and the individual’s activity level. Conservative treatments may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with anti-inflammatory medications to manage pain and swelling. Physical therapy can help improve knee function and strength.
Prolotherapy, involving the injection of a regenerative solution into the tendon, can aid in healing the meniscus by providing essential nutrients directly to the affected area. Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe tears that do not respond to conservative treatments. Surgical options range from meniscus repair to partial meniscectomy, where damaged tissue is either repaired or removed.
The recovery timeline for a torn meniscus varies among individuals based on factors such as the tear’s severity and the chosen treatment approach. Adhering to a prescribed rehabilitation plan and following medical advice are crucial for a successful recovery. While some patients may return to normal activities relatively quickly, others may require more time for full recovery.
Early intervention and appropriate treatment can help prevent further damage to the knee joint and promote a smoother recovery process. Seeking medical attention upon suspecting a meniscal tear is essential to receive timely care and support for optimal healing.