Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
Vaginal tears and cuts can occur due to various reasons, including sexual activity, hair removal, and childbirth. While minor vaginal wounds are usually harmless and heal on their own, more severe tears may require medical attention. In this article, we delve into the common causes of vaginal tears, the different types of tears, and how they can be treated and prevented.
One of the common causes of vaginal tears is sexual activity. Friction or dryness during intercourse can damage the delicate tissues of the vagina, leading to tears. Factors such as rough thrusting, vaginal dryness, and certain skin conditions can increase the likelihood of tears during sex. Additionally, hair removal methods like shaving or waxing can also cause cuts or tears in the vaginal area.
There are different degrees of vaginal tears based on their severity:
First-degree tears are the least severe and involve the skin around the vaginal opening and perineum. They may or may not require stitches and typically heal within a few weeks.
Second-degree tears extend into the muscle tissue between the vaginal opening and rectum. Stitches are usually required for these tears, and healing may take 3 to 4 weeks.
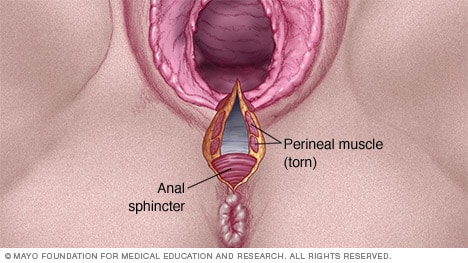
Third-degree tears involve the anal sphincter muscle, while fourth-degree tears extend into the rectal mucous membrane. These tears are more severe and may require repair in an operating room. Healing for third and fourth-degree tears can take 4 to 6 weeks or longer.
For minor vaginal cuts or tears, keeping the area clean and dry is essential for healing and preventing infections. Basic care includes washing the area with mild soap, avoiding harsh products, and using pain relievers if needed. It’s advisable to avoid sexual activities involving the vagina during the healing process.
To prevent vaginal tears, especially during sex, it’s important to prioritize arousal, engage in foreplay, and use adequate lubrication. Using water or silicone-based lubricants can reduce friction and lower the risk of tears. For hair removal, following proper techniques and precautions can help prevent cuts and injuries.
If a vaginal tear is deep, extensive, or shows signs of infection, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Excessive bleeding, persistent pain, or concerning symptoms like fever, foul-smelling discharge, or numbness should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider. Prompt treatment can prevent complications and ensure proper healing.
By understanding the causes, types, and appropriate care for vaginal tears, individuals can take proactive steps to promote vaginal health and well-being. Prioritizing self-care, seeking medical advice when needed, and practicing safe and gentle intimate practices can contribute to a healthy vaginal environment.