Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents [hide]
Otitis media, commonly known as a middle-ear infection, refers to an infection located behind the eardrum. This type of ear infection can occur following conditions that obstruct fluid drainage from the middle ear, such as allergies, colds, sore throats, or respiratory infections. While middle-ear infections are prevalent in children, they can also affect adults. In adults, an ear infection may indicate a more severe issue than in children, necessitating additional tests and medical attention.
There are several ways in which infections can impact the middle ear:
Acute otitis media is a sudden middle-ear infection characterized by swelling and redness. It leads to the accumulation of fluid and mucus inside the ear, accompanied by symptoms like fever and ear pain.
Following the resolution of an infection, fluid and mucus can build up in the middle ear, causing a sensation of fullness. This condition may persist for months, potentially affecting hearing.
In chronic otitis media with effusion, fluid remains in the middle ear for an extended period or recurs despite the absence of infection. This type of middle-ear infection can be challenging to treat and may impact hearing.
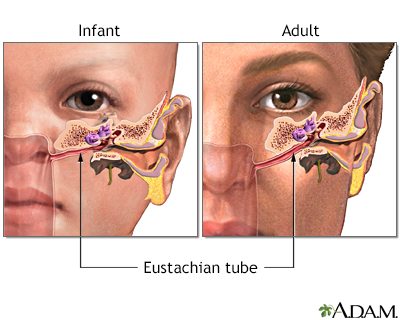
Individuals are more susceptible to ear infections if they smoke or are exposed to smoke, experience seasonal or year-round allergy symptoms, or have a cold or upper respiratory infection. The eustachian tube, connecting the middle ear to the throat, plays a crucial role in regulating pressure. Conditions like colds or allergies can inflame the tube, hindering fluid drainage and leading to the growth of bacteria and viruses that cause middle-ear infections.
Common symptoms of a middle-ear infection in adults include ear pain, fluid drainage, muffled hearing, and a sore throat. In some cases, individuals may experience a fever and balance issues. Diagnosis involves a medical history review, physical examination, otoscope inspection of the ear, and tests like tympanometry and hearing assessments with a tuning fork.
Treatment for a middle-ear infection in adults may include antibiotics, pain medication, decongestants, or nasal steroids. In cases where symptoms persist, further medical intervention may be necessary to prevent complications like head infections, hearing loss, or facial nerve paralysis. In some instances, the placement of ear tubes through surgery may be recommended to facilitate fluid drainage and relieve pressure in the middle ear.
An ear infection, also known as acute otitis media, affects the middle ear, which contains the ear’s tiny vibrating bones behind the eardrum. While children are more prone to ear infections, adults can also experience them. Symptoms of an ear infection include ear pain, fluid drainage, and hearing difficulties. Prompt medical attention is essential if symptoms persist or worsen.
Children may exhibit signs like ear pain, tugging at the ear, trouble sleeping, fever, and fluid discharge. Adults commonly experience ear pain, fluid drainage, and hearing issues. Seeking medical advice is crucial if symptoms last more than a day, are severe, or involve discharge of fluid or pus from the ear.
Ear infections typically result from bacterial or viral infections in the middle ear, often triggered by conditions like colds, flu, or allergies that cause congestion and swelling. Factors like age, group child care, seasonal influences, and exposure to secondhand smoke can increase the risk of ear infections.
While most ear infections resolve without lasting issues, recurrent infections can lead to complications such as hearing impairment, speech delays, or the spread of infection to surrounding tissues. Preventive measures include promoting good hygiene practices, avoiding secondhand smoke, breastfeeding infants, and staying up to date on vaccinations.
Managing ear infections at home involves alleviating pain and discomfort:
Consulting a pharmacist for ear infection symptoms can lead to recommendations for eardrops or other treatments to manage the condition effectively without immediate GP intervention.