Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
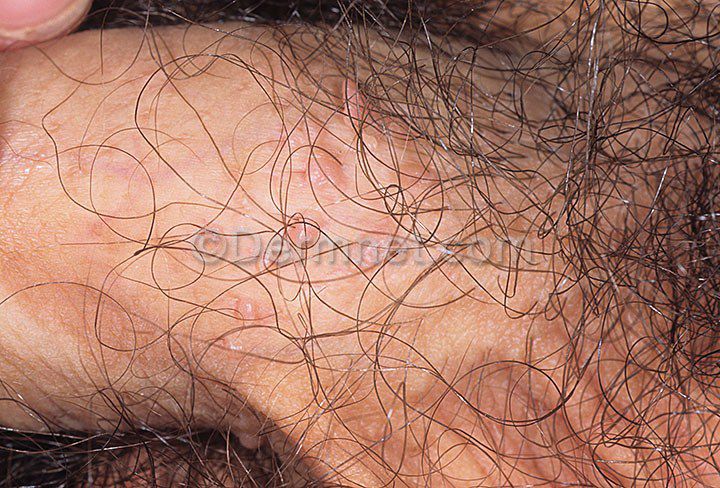
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection that can manifest in various ways on the skin. In some cases, HPV can lead to the development of genital warts in males. These warts may appear as raised bumps or growths on or around the genital area, including the anus. However, it is important to note that most males with HPV do not experience any visible symptoms.
Most men infected with HPV do not exhibit any symptoms, making it challenging to detect the virus without specific medical examinations. However, when symptoms do occur, they typically present as genital warts. These warts can vary in appearance, including being small or large, raised or flat, and may resemble a cauliflower-like cluster. Genital warts caused by HPV do not usually cause pain but can be visually unappealing.
It is essential for men to be vigilant about any new or unusual growths, lumps, or sores on their penis, scrotum, anus, mouth, or throat, as these could be potential signs of HPV infection. While most HPV infections resolve on their own without causing health problems, persistent HPV can lead to genital warts or certain types of cancer.
Diagnosing HPV in males often involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider to inspect for any visible warts or symptoms. In some cases, a healthcare professional may conduct an HPV DNA test to confirm the presence of the virus. Additionally, procedures such as biopsies or oral swabs may be performed to further evaluate HPV infection.
While there is no specific cure for HPV, treatments are available to manage symptoms and complications associated with the virus. These treatments may include topical medications, cryotherapy, electrocautery, or surgical excision to remove genital warts. Early detection and treatment of HPV-related health issues, such as genital warts or cancer, can improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Preventative measures play a crucial role in lowering the risk of contracting HPV and reducing the transmission of the virus to others. Vaccination against HPV is highly effective in preventing certain strains of the virus that can cause genital warts and various cancers. The HPV vaccine is recommended for individuals aged 9 to 45 and is particularly beneficial when administered before the onset of sexual activity.
Aside from vaccination, using condoms correctly during sexual activity can help reduce the risk of HPV and other sexually transmitted infections. Regular communication with sexual partners about sexual health and potential risks is also essential in preventing the spread of HPV.
While HPV may not always present visible symptoms in males, being aware of the potential signs of infection, such as genital warts, is crucial for early detection and treatment. Understanding how HPV can manifest on the skin and taking proactive steps to prevent and manage the virus can help individuals maintain their sexual health and well-being.