Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents [hide]
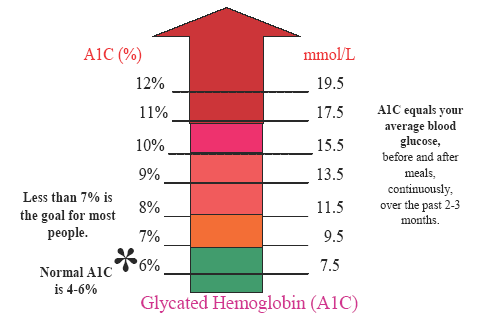
An A1C test is a crucial tool in diagnosing and managing diabetes, providing insights into a person’s average blood sugar levels over the past three months. This test measures the percentage of hemoglobin proteins that are glycated, indicating the amount of glucose present in the blood. For individuals without diabetes, a normal A1C level is below 5.7%, while a range of 5.7% to 6.4% signals prediabetes. A level of 6.5% or higher usually indicates Type 2 diabetes.
For individuals already diagnosed with diabetes, regular A1C tests are essential to assess the effectiveness of their management plan. An A1C level below 7% is generally considered a good target for most adults with diabetes. However, personal A1C goals may vary based on factors such as age, existing complications, and overall health status. It’s crucial to work closely with healthcare providers to set and achieve individualized A1C targets.
While an A1C level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes, dangerous levels of A1C are typically considered to be 9% and above. A high A1C level significantly increases the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes, including kidney disease, eye issues, cardiovascular problems, neuropathy, and metabolic syndrome. Maintaining A1C levels below 7% is crucial for reducing the likelihood of these complications.
Several factors can influence the accuracy of A1C test results, leading to falsely high or low readings. Conditions such as genetics, specific hemoglobin variants, medical issues, certain medications, and errors in testing procedures can impact A1C levels. It’s important to consider these factors when interpreting A1C results and to consult with healthcare providers for a comprehensive assessment.
Individuals aiming to lower and maintain their A1C levels can adopt various strategies, including adhering to prescribed treatment plans, engaging in regular physical activity, following a healthy diet, quitting smoking (if applicable), and seeking diabetes education and support services. By actively managing A1C levels through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, individuals can enhance their overall diabetes care and reduce the risk of complications.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of A1C levels in diabetes management is crucial for individuals to monitor their blood sugar control effectively. By recognizing the implications of different A1C ranges, identifying dangerous levels, and implementing targeted strategies to improve A1C levels, individuals can proactively manage their diabetes and enhance their quality of life. Regular A1C testing, in conjunction with a comprehensive healthcare approach, plays a vital role in optimizing diabetes care and reducing the risk of associated complications.