Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents [hide]
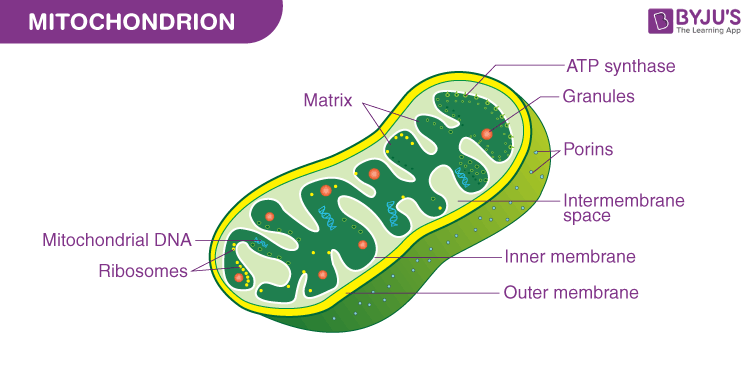
The mitochondria are essential membrane-bound organelles within cells that play a crucial role in energy production. These organelles have a unique structure with two membranes, which is uncommon among intercellular organelles. The primary function of mitochondria is to generate energy through a process known as oxidative phosphorylation. This process involves converting chemicals within the cell into energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which serves as a high-energy bond providing energy for various cellular reactions.
Cells have varying amounts of mitochondria depending on their energy requirements. For instance, tissues with high energy demands, such as muscle, liver, kidney, and the brain, contain a significant number of mitochondria. These organelles are vital for providing the energy needed for the proper functioning of these tissues. Any defects in the pathways involved in mitochondrial function can lead to symptoms affecting different parts of the body, including muscles, the brain, and kidneys, resulting in various health conditions.
Research on mitochondria has been a significant focus in biomedical studies due to their critical role in cell physiology and pathology. Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with aging and age-related diseases, impacting processes such as ATP synthesis, calcium homeostasis, metabolic pathways, and radical production. Despite advancements in understanding mitochondria, there is still much to learn about the mechanisms and regulation of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide formation by these organelles.
Studies have shown that mitochondria are involved in various physiological and pathological processes, making them a subject of extensive research. The relationship between mitochondria and cell physiology, pathology, medicine, and disease has garnered significant interest in the scientific community. Mitochondria’s functions in energy metabolism, apoptosis, radical production, aging, and disease have led to a surge in research publications related to these organelles.
While the primary function of mitochondria is to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, they also play crucial roles in ion homeostasis, metabolic pathways, apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and consumption. These functions are essential for maintaining cellular health and proper physiological processes. Mitochondria are central to carbon metabolism, serving as key players in both catabolic and anabolic processes.
Additionally, mitochondria are involved in nitrogen metabolism, haem synthesis, iron-sulphur cluster formation, and the biosynthesis of essential biomolecules. They also play a significant role in programmed cell death by activating caspases and triggering apoptotic pathways. Dysfunction in any of these mitochondrial functions can contribute to age-related diseases and other pathologies.
The mitochondrial free radical theory of aging proposes that ROS generated by mitochondria during oxidative metabolism are the primary cause of cellular damage, leading to aging and age-related diseases. Mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production can result in damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA, contributing to cellular dysfunction and disease development. While there is evidence supporting this theory, the exact role of mitochondrial ROS in aging and disease remains a topic of ongoing research.
Identifying and quantifying specific sites within mitochondria that generate ROS is crucial for understanding their impact on aging and age-related diseases. By studying these sites, researchers aim to manipulate ROS production to potentially mitigate the effects of mitochondrial dysfunction on cellular health.
Research has identified several sites within mitochondria that are responsible for the production of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide during oxidative phosphorylation. These sites include enzymes in the citric acid cycle, ubiquinone reduction pathways, and the electron transport chain. Understanding the maximum capacities of these sites in generating ROS is essential for elucidating their role in cellular physiology and pathology.
Studies have shown that different sites within mitochondria have varying capacities for superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production. For example, site IIIQo exhibits the highest capacity for ROS production, followed by sites IQ and IIF. The relative importance of these sites may vary depending on the tissue and species under investigation. By studying these sites, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms of ROS generation and their implications for cellular function.