Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
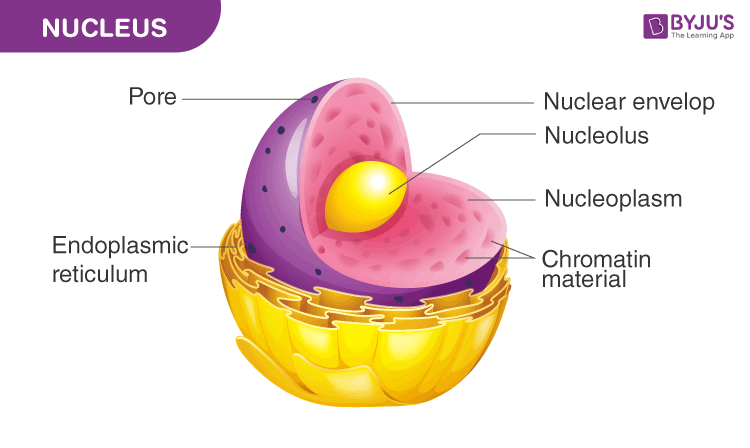
The nucleus is a vital organelle found in most cells, except for bacteria and blue-green algae. It is separated from the rest of the cell by a double-layered nuclear membrane, which is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. This organelle plays a crucial role in controlling and regulating the activities of the cell, such as growth and metabolism, as it houses the genetic material of the cell, including DNA and genes.
One of the primary functions of the nucleus is to serve as the information center of the cell. The genetic code stored in the DNA is transcribed into messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) molecules. Each mRNA molecule carries the information for a specific protein and is transported out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, these mRNA molecules are translated into proteins, which are essential for various cellular functions.
The nucleus plays a crucial role in gene expression by regulating the transcription and translation processes. DNA replication, transcription, and RNA processing occur within the nucleus, while the final stage of gene expression, translation, takes place in the cytoplasm. The nuclear envelope separates the genome from the cytoplasm, allowing for the regulation of gene expression through unique mechanisms specific to eukaryotic cells.
Unlike prokaryotic cells where mRNA translation can occur simultaneously with transcription, eukaryotic mRNA undergoes posttranscriptional processing, such as splicing, before being transported to the cytoplasm. This posttranscriptional regulation allows for more intricate control of gene expression, including mechanisms like alternative splicing.
Within the nucleus, there are specialized structures like the nucleolus, which is involved in ribosome production. The nucleoplasm, a gel-like matrix, suspends the nuclear components and provides a medium for various nuclear activities. The nuclear lamins, intermediate filament proteins, contribute to the structural organization and function of the nucleus.
Studies have shown that nuclear lamins are essential for normal nuclear function, playing roles in epigenetics, chromatin organization, DNA replication, transcription, and DNA repair. Mutations in lamin proteins have been linked to various diseases, highlighting the importance of these proteins in maintaining nuclear integrity and function.
During cell division, the nucleus plays a critical role in ensuring that each daughter cell receives the necessary genetic material. The nucleus is the first organelle to divide, ensuring that the daughter cells have the correct number of chromosomes and genes. This process is essential for maintaining genetic stability and passing on hereditary information to the next generation of cells.
Some cells, like human red blood cells, lose their nuclei upon maturation. This loss of the nucleus allows these cells to carry out their specialized functions more efficiently. However, in most cells, the nucleus remains a central hub for genetic information and cellular regulation.
In conclusion, the nucleus is a vital organelle that serves as the control center of the cell. By housing the genetic material and controlling gene expression, the nucleus plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular functions and regulating various processes within the cell. Understanding the functions of the nucleus is essential for unraveling the complexities of cellular biology and advancing our knowledge of how organisms develop and function.