Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
The population of the world has been a subject of fascination and concern for centuries. From the early days of human civilization to the modern era, the world population has experienced significant growth and change. Let’s delve into the historical data and projections to understand the past, present, and future of the world’s population.
At the dawn of agriculture around 8000 B.C., the world’s population was estimated to be around 5 million. By 1 A.D., it had grown to approximately 200 million, with some estimates suggesting even higher numbers. The industrial revolution marked a turning point, propelling the population growth to unprecedented levels. It took thousands of years to reach the first billion, but subsequent billions were added at a much faster pace.
By the end of the 20th century, the world population had surged from 1.65 billion to 6 billion. The growth rate peaked in the late 1960s at around 2% and has since declined. As of 2024, the world population stands at over 8 billion, with an estimated annual growth rate of 0.91%.
The current growth rate indicates that the world population is expected to reach 9 billion by 2037 and 10 billion by 2057. The projections suggest a gradual slowdown in population growth compared to previous decades. By 2100, the world population is estimated to reach 10.4 billion.
Various factors such as fertility rates, life expectancy, and migration patterns influence population dynamics. While some regions are experiencing rapid growth, others are facing demographic challenges such as aging populations and declining birth rates.
The distribution of the world population across different regions provides valuable insights into global demographics. Here is a snapshot of population trends in key regions:
With a population of over 4.75 billion in 2024, Asia remains the most populous continent. The region’s growth rate, fertility rate, and median age play crucial roles in shaping global population trends.
Africa has been experiencing rapid population growth, with over 1.46 billion people in 2024. The continent’s youthful population and high fertility rates contribute significantly to its demographic landscape.
Europe, with a population of around 742 million, faces demographic challenges such as low fertility rates and an aging population. These factors have implications for the region’s future population dynamics.
North America, home to approximately 378 million people, exhibits diverse population trends across countries like the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Migration patterns and fertility rates influence population growth in the region.
Aside from regional variations, the world population is characterized by religious and cultural diversity. Different faiths and belief systems shape the demographic landscape in various countries. Here is a glimpse of the global population by religion:
With over 2.1 billion followers, Christianity remains the largest religion globally. The faith is divided into various denominations, including Catholicism, Protestantism, and Orthodox Christianity.
Islam, with around 1.6 billion adherents, is the second-largest religion in the world. The Sunni and Shia branches represent the majority of Muslim populations worldwide.
Hinduism, Buddhism, and other faiths contribute to the religious diversity of the world population. These belief systems have millions of followers globally, with significant concentrations in specific regions.
Examining the population data by country provides a detailed understanding of demographic trends at a national level. Here are some key insights into the population of select countries:
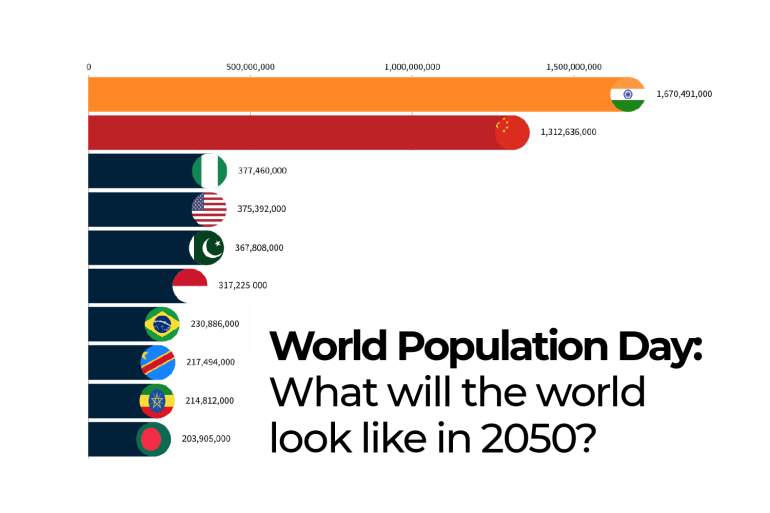
With a population exceeding 1.4 billion, India is the second-most populous country globally. Factors such as fertility rates, urbanization, and healthcare infrastructure influence India’s demographic landscape.
China, with a population of over 1.4 billion, has implemented various population control measures over the years. The country’s demographic policies and economic development impact its population growth.
The United States, with around 340 million people, experiences population growth driven by factors like immigration, birth rates, and cultural diversity. The country’s demographic trends have implications for various sectors, including healthcare and labor.
By analyzing historical data and current projections, we can gain valuable insights into the complex and dynamic nature of the world’s population. Understanding population trends is essential for policymakers, researchers, and organizations to address global challenges and plan for a sustainable future.