Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents [hide]
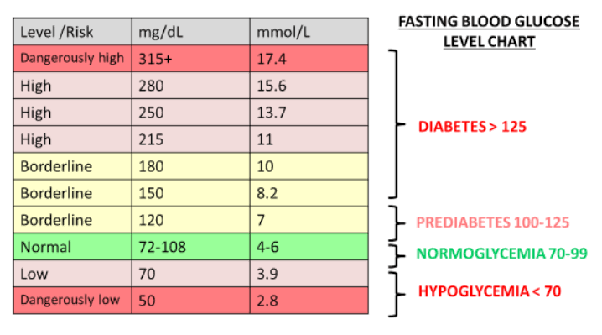
Blood sugar levels play a crucial role in maintaining overall health, especially for individuals with diabetes. It is essential to be aware of the ideal blood sugar range and understand the potential risks associated with high or low blood sugar levels. In this article, we will delve into the significance of blood sugar levels, the causes of imbalances, symptoms to watch out for, and appropriate actions to take when blood sugar levels become dangerous.
Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, can occur due to various factors such as taking too much insulin, inadequate carbohydrate intake in relation to insulin dosage, timing of insulin administration, physical activity, alcohol consumption, and meal composition. Other factors like weather conditions, changes in routine, high altitude, puberty, and menstruation can also contribute to low blood sugar levels.
Recognizing the symptoms of low blood sugar is crucial as they can vary from person to person. Common signs include a fast heartbeat, shaking, sweating, nervousness, dizziness, and hunger. However, some individuals may experience hypoglycemia unawareness, where they do not exhibit any symptoms even at dangerously low blood sugar levels.
Low blood sugar can occur at any time of the day, including nighttime. Factors such as physical activity before bedtime, excessive insulin intake, and alcohol consumption in the evening can lead to nighttime hypoglycemia. It is essential to eat regular meals and have a snack before bed to prevent low blood sugar while sleeping. Severe low blood sugar, characterized by weakness, difficulty walking, confusion, and seizures, typically occurs when blood sugar levels drop below 54 mg/dL.
On the other end of the spectrum, high blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can have serious consequences if left untreated. Individuals with diabetes may experience hyperglycemia when their blood sugar levels rise above 240 mg/dL. Prolonged high blood sugar can lead to a condition called ketoacidosis, which is characterized by the accumulation of ketones in the blood, making it more acidic.
Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fats due to insufficient insulin levels. If not addressed promptly, ketoacidosis can result in diabetic coma, necessitating immediate medical intervention. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and taking appropriate actions are essential in managing high blood sugar levels.
For individuals experiencing low blood sugar, treatment options include consuming glucose tablets, fruit juice, soda, or hard candy to raise blood sugar levels. It is crucial to retest blood sugar after 15 minutes and continue treatment until levels normalize. In cases of hyperglycemia, monitoring ketone levels and seeking medical attention if levels are elevated is vital.
Hydration, physical activity, stress management, adequate sleep, and carbohydrate counting are essential strategies to help regulate blood sugar levels. Consulting a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on managing blood sugar is recommended, especially for individuals with diabetes or prediabetes.
Diabetes is a serious condition that requires careful monitoring and management of blood sugar levels. If you have concerns about your blood sugar levels or experience persistent symptoms of high or low blood sugar, it is important to consult a healthcare provider. Regular check-ups, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications can significantly impact blood sugar control and overall well-being.
By staying informed about the dangers of blood sugar imbalances and taking proactive measures to maintain healthy levels, individuals can mitigate the risks associated with fluctuations in blood sugar. Prioritizing blood sugar management is key to preventing long-term complications and promoting optimal health.