Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Contents
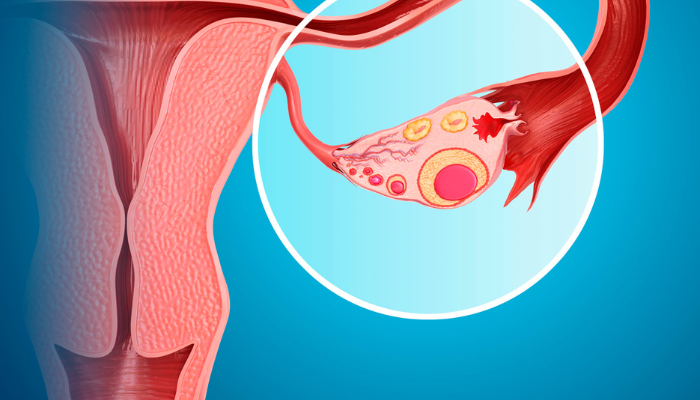
Ovarian cysts are a common occurrence in individuals with ovaries, typically harmless and resolving on their own. However, there are instances where these cysts can grow larger, persist, and lead to complications. It is essential to understand the potential risks associated with ovarian cysts, particularly in determining what size of ovarian cyst can be considered dangerous.
Ovarian cysts can vary in type and origin, with some common forms including functional cysts, endometriomas, and dermoid cysts. Functional cysts, such as follicular and corpus luteal cysts, are a natural part of the menstrual cycle. Endometriomas are associated with endometriosis, while dermoid cysts can contain various tissues like hair and skin.
These cysts can develop due to follicle abnormalities, hormonal imbalances like in polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), or even genetic factors. Understanding the underlying cause of ovarian cyst formation is crucial in determining the appropriate management and treatment.
While most ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, larger cysts or those with abnormal features can present with symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular menstruation. It is important to monitor cysts that are growing in size or causing discomfort to rule out potential complications like ovarian torsion or malignancy.
There is a slight increased risk of ovarian cancer associated with certain types of ovarian cysts, especially in individuals with a family history of ovarian or related cancers. Regular monitoring and evaluation are essential in assessing the risk factors and determining the appropriate course of action.
Diagnosing ovarian cysts often involves pelvic exams, imaging tests like ultrasounds, and sometimes blood work to assess hormonal levels. Treatment options range from watchful waiting for small, asymptomatic cysts to surgical intervention for larger or problematic cysts.
Medications like hormonal birth control may be prescribed to manage recurring cysts, while surgical procedures like laparoscopic cystectomy are performed for cysts that require removal. Early detection and intervention play a crucial role in preventing complications and ensuring optimal reproductive health.
While ovarian cysts cannot always be prevented, maintaining overall gynecological health through regular check-ups and screenings can help in early detection and management. Understanding the symptoms and risks associated with ovarian cysts is key in promoting proactive healthcare practices.
Individuals experiencing persistent pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, or other concerning symptoms should seek medical attention promptly to address any underlying issues related to ovarian cysts. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can take control of their reproductive health and well-being.